In today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape, understanding the nuances between traditional banks and emerging neobanks is crucial. This article delves into the key differences that distinguish these two banking models, exploring their respective advantages and disadvantages to help you make informed financial decisions. We’ll compare banks and neobanks across various factors, including account access, fees, features, regulations, and overall customer experience, providing a comprehensive overview of their distinct characteristics.
Are you curious about the differences between a bank and a neobank? This comprehensive comparison will clarify the distinctions between these two financial institutions. We’ll explore the key differences in their services, from the convenience of online banking offered by neobanks to the established infrastructure of traditional banks. Understanding these key differences is vital for choosing the financial institution that best suits your individual needs. We will examine how banks and neobanks operate, highlighting their unique features and benefits. Whether you prioritize digital accessibility or physical branch presence, this article will provide the necessary information to make an informed choice between banks and neobanks.
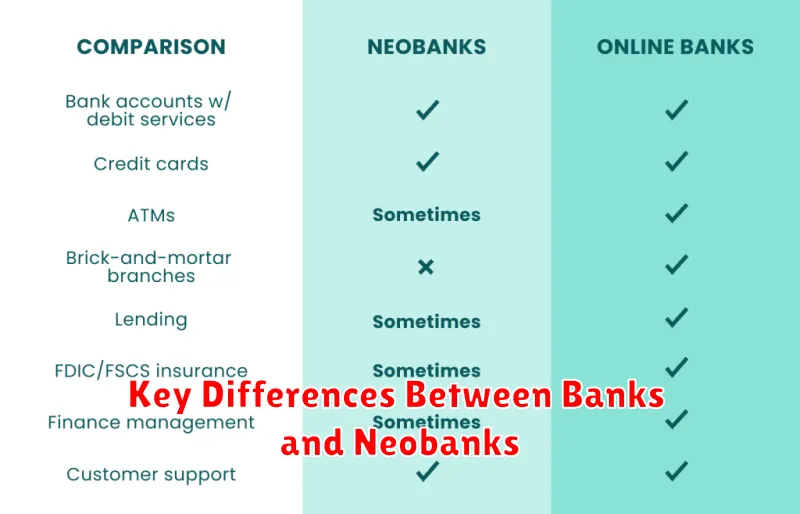
What Is a Neobank?
A neobank is a financial technology (fintech) company that offers digital and mobile-first financial solutions, often without physical branches. They provide services similar to traditional banks, such as checking and savings accounts, money transfers, and payment cards, but operate exclusively online or through mobile apps.
Neobanks partner with traditional banks or other licensed financial institutions to hold customer deposits and offer regulated financial products. This partnership allows them to offer the convenience and innovation of a tech company while adhering to financial regulations.
Neobanks often target specific demographics, such as tech-savvy millennials or small businesses, with tailored services and user-friendly interfaces.
Licensing and Regulation
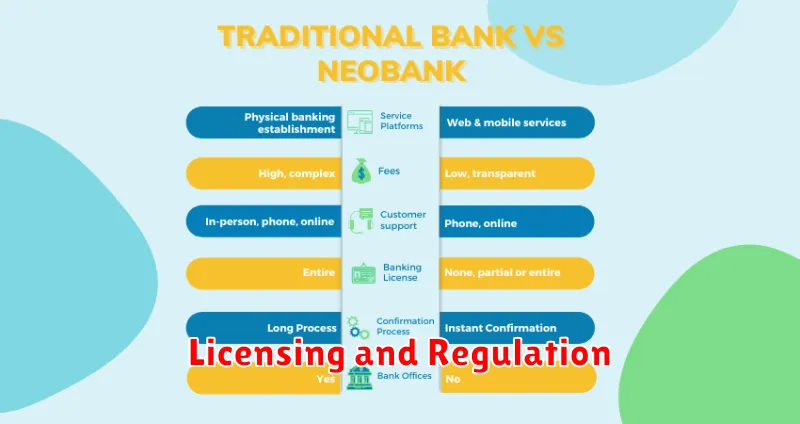
A key distinction between traditional banks and neobanks lies in their licensing and regulatory frameworks. Traditional banks hold full banking licenses, granting them the authority to accept deposits and offer a full suite of financial services. These licenses necessitate compliance with stringent regulatory oversight, including reserve requirements and capital adequacy ratios.
Neobanks, however, take a varied approach. Some partner with established banks to offer their services, leveraging the partner’s existing license. This allows them to operate under the umbrella of the partner bank’s regulatory coverage. Other neobanks pursue their own banking licenses, thus becoming subject to the same rigorous regulations as traditional banks. The specific regulatory landscape depends on the jurisdiction where the neobank operates.
This difference in licensing can impact the range of services offered and the level of consumer protection. Customers should be aware of whether their neobank holds a license independently or operates through a partnership.
Fee Structures Comparison
A key differentiator between traditional banks and neobanks lies in their fee structures. Traditional banks often have a wider range of fees, including monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees, ATM fees (especially out-of-network), and international transaction fees. These fees can significantly impact account holders, particularly those with lower balances.
Neobanks, on the other hand, generally aim for a more transparent and often less expensive fee structure. Many neobanks pride themselves on having no monthly maintenance fees, limited or no overdraft fees, and access to wider ATM networks without incurring charges. They frequently offer free international transactions, making them an attractive option for travelers and those involved in international commerce.
| Fee Type | Traditional Bank | Neobank |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Maintenance | Often charged | Typically none |
| Overdraft | High fees common | Limited or none |
| ATM | Out-of-network fees frequent | Wider networks, often free |
| International Transaction | Typically charged | Often free |
Service Limitations and Strengths
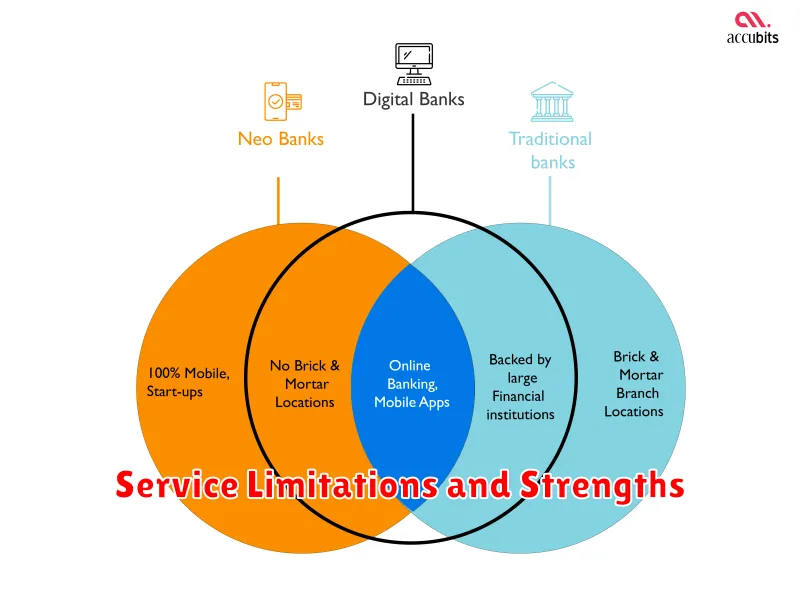
Both traditional banks and neobanks have their own set of limitations and strengths regarding the services they offer. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right financial institution for your needs.
Traditional Banks
Strengths: Traditional banks typically offer a wider range of services, including complex financial products like mortgages, loans, and wealth management. They also have a physical presence with branch networks, providing in-person support for those who prefer it.
Limitations: Traditional banks often come with higher fees and may have more stringent requirements for account opening. Their technological innovation may also lag behind neobanks.
Neobanks
Strengths: Neobanks excel in technological innovation, offering user-friendly mobile apps, lower fees, and often more competitive interest rates. Their 24/7 digital accessibility provides greater convenience for managing finances.
Limitations: Neobanks may offer a limited range of services, often lacking physical branches and complex financial products. Some may also have restrictions on account types or eligibility.
Security and Data Handling
A crucial distinction between traditional banks and neobanks lies in their approach to security and data handling. Both entities are subject to stringent regulations, but their implementation strategies differ. Traditional banks typically rely on established, often complex, security infrastructure built over time. They prioritize physical security measures alongside digital ones.
Neobanks, being digitally native, leverage cloud technology and advanced data analytics for security. This allows for more agile responses to threats and potentially more personalized security measures. However, the reliance on third-party cloud providers can introduce new vulnerabilities. Data privacy remains a primary concern for both, although the types of data collected and how it’s utilized may differ. Neobanks often collect more granular data on customer spending habits to offer personalized financial insights.
Regulatory compliance is paramount for both. While traditional banks have a long history of navigating regulations, neobanks are constantly adapting to the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding fintech.
Which One Fits Your Needs?
Choosing between a traditional bank and a neobank depends entirely on your individual financial needs and priorities. Consider the following to determine the best fit:
Traditional Banks
Opt for a traditional bank if you value in-person service, require access to a wider range of financial products like loans and mortgages, or prefer the established security of a physical institution. Stability and a comprehensive suite of services are key advantages.
Neobanks
Choose a neobank if you prioritize digital convenience, lower fees, and innovative features like budgeting tools and real-time spending notifications. Tech-savviness and a desire for streamlined banking are important considerations.
Making Your Decision
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual circumstances. Carefully weigh the pros and cons of each option before making a decision.